What is Powder & Granule II
Writer: admin Time:2020-05-23 13:55 Browse:℃
1. Mixing
1) Definition
Mixing is a process during which two or more ingredients are uniformly distributed. Its goal is to uniform ingredient content.
2) Meaning:
a. Mixing can influence preparation quality, leading to tablet spot, unqualified disintegration time and unqualified hardness;
b. Mixing can also affect content uniformity, which will make toxic medicine, medicine being taken for a long term and medicine of concentration approaching toxic concentration to be threatening.
3) Mixing principle:
a. Convection mixing: general mixing of obvious displacement;
b. Shear mixing: internal force generating sliding surface; partial mixing;
c. Diffusion mixing: transposition between neighbor granules; partial mixing.
4) Mixing method
Blend mixing, grind mixing and sieve mixing
5) Mixing equipment:
a. Rotary container: horizontal cylinder mixer, V type mixer, double cone mixer
b. Fixed container: groove blender; conical auger mixer
6) Factors influencing mixing
|
Dose |
Target weight |
Dispersion |
|
0.1-0.01g |
1-0.1g |
10 times |
|
0.01-0.001g |
1-0.1g |
100 times |
|
<0.001g |
1-0.1g |
1000 times |
b. Ingredient density
If density of ingredients differs a lot, material of low density can be filled first, followed by materials of high density.
c. Ingredient adhesion and electricity
Generally, medical powder or excipients of large dose or low adhesion are filled before material of small dose or strong adhesion;
During mixing and friction, surface charge might be generated and will affect the process. Static electricity can be eliminated by adding some surface active agent, lubricant or wetting material.
d. Containing liquid or hygroscopic ingredient
Liquid contained in formula can be absorbed by other ingredients or absorbent (such as calcium phosphate and sucrose...)
If hygroscopic ingredients are contained, corresponding measures should be taken before mixing for uniform mixing.
e. Containing ingredients which can form eutectic mixture
According to practical situation, the mixing ratio in which eutectic mixture can be generated should be avoided.
7) Dose splitting
It refers to the process in which uniformly mixed powder is split to dose of the same weight.
Method: visual method, weighing method and volume method (the commonest in mechanical mass production)
8) Quality inspection
a. Granularity: more than 95% powder can pass through #7 screen and Chinese medical powder passes through #6 screen.
b. Uniformity: putting samples of proper weight on a piece of smooth paper and covering about 5cm2, flattening their surface and observing in bright place. The powders should be uniform and have no stain.
c. Drying and weight losing: lost weight cannot exceed 2% except special regulation and moisture content cannot exceed 9%.
d. Filling difference
e. Hygroscopicity
When water vapor pressure in air is larger than that of medical powder, powder will absorb moisture.
Medicine’s hygroscopicity can be indicated by a hygroscopic balance curve. Moisture absorption can be calculated for medicines in different humidity. Then the hygroscopic balance curve can be drawn according to moisture absorption to relative humidity.
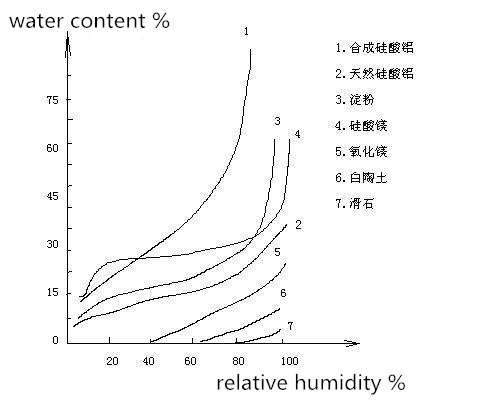
Insoluble medicine
Synthetic aluminum silicate
Natural aluminum silicate
Starch
Magnesium silicate
Magnesium oxide
Kaolin
Soluble medicine
1-Urea
2-Citric acid
3-Tartaric acid
4-Sodium parasalicylate
It can be found that soluble medicine hardly absorbs moisture in low relative humidity, while moisture absorption increases dramatically in a relative particular humidity, which is called critical relative humidity (CRH). Soluble medicine has stable CRH value. The larger CRH is , the more difficult it is for the medicine to absorb moisture.
Elder Hypothesis on moisture absorption
CRH of mixture is approximately the product of the CRH of drug substances, i.e., CRHAB≈CRHA*CRHB, but has nothing to do with the proportion of all substances;
Elder Hypothesis is suitable for soluble medical mixture, but not for medicines which interact with each other or have common ion;
Insoluble medicine has no certain CRH.
The meaning to measure CRH
CRH value can be used to indicate medicine’s moisture absorption performance. Generally, medicine of larger CRH is more difficult to absorb moisture;
Conditions for production and storage should be controlled. Especially, the relative humidity should be kept under CRH to avoid moisture absorption;
CRH can be for reference to select moisture-proof excipients. Material of large CRH is usually used as excipients.
2. Granules
1) Definition
Granules are dry granular preparation of certain granularity,being made from drug substance and proper excipients.
2) Granularity range
The content of granules which can pass #5 screen but not #1 screen is no more than 15%. Granules of size within 105-500μm is also called fine granules.
3) Classification
a. Soluble granules: Cefalexin Penicillin Granules;
b. Suspending granules: Roxithromycin granules;
c. Effervescent granules: Compound calcium carbonate effervescent granules.
d. In pharmacopoeia:
a) Sustained-release granules: Ketoprofen sustained-release granules;
b) Controlled-release granules
c) Enteric granules: Omeprazole enteric granules
4) Features (compared with powders)
a. Dispersion, adhesiveness, agglomeration and weak moisture absorption;
b. Convenient taking;
c. If necessary, granules can be coated to be moisture-proof, sustained-released or enteric.
5) Production
Crushing → sieving → mixing
→ mixture (agglomerating when gripped and dispersing when pressed)
→ wet granulation (squeezing granulation, fluid bed granulation)
→ granule drying
→ milling and sizing
→ dose splitting → packing
6) Quality inspection
a. Appearance
b. Granularity: The content of granules which can pass #5 screen but not #1 screen is no more than 15% (5 sachets of monodose, or 1 sachet of multi-dose)
c. Drying and weight reduction: no more than 2%
d. Solution check:
a) Soluble granules: 10g granules, 200ml hot water, mixing for 5min; soluble granules should solve or the solution is slight turbid;
b) Effervescent granules: 3 sachets in 200ml water of normal temperature; generating gas and being effervescent rapidly; granules should disperse or dissolve in water in 5min completely;
c) Suspending granules: dissolution rate measuring but not solubility checking.
e. Filling difference
f. Hygienic examination

