What is tablet III
Writer: admin Time:2020-05-23 10:25 Browse:℃
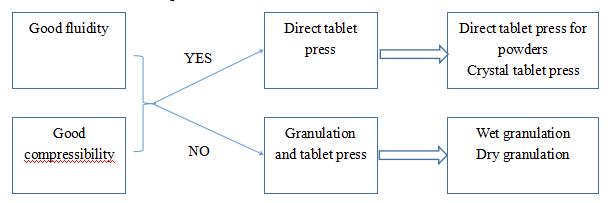
8.Granulation and tablet press
1) Granulation
It is a process during which powder, melt liquid, aqueous solution and other materials are processed into granules of specific shape and size.
2) Granulation goal
a. For better fluidity
b. To avoid ingredient isolation
c. To prevent dust from flying and sticking to device wall
d. To adjust bulk density and improve dissolution performance
e. To change uniform force transmission during tablet production
3) Granulation method
a. Wet granulation
b. Dry granulation
c. Other method: spraying granulation
4) Wet granulation
Liquid adhesive is added into powdery materials and agglomerates powder through adhesive bridging or adhesion. Agglomerated powder is then split into granules of specific size and shape under mechanical force.
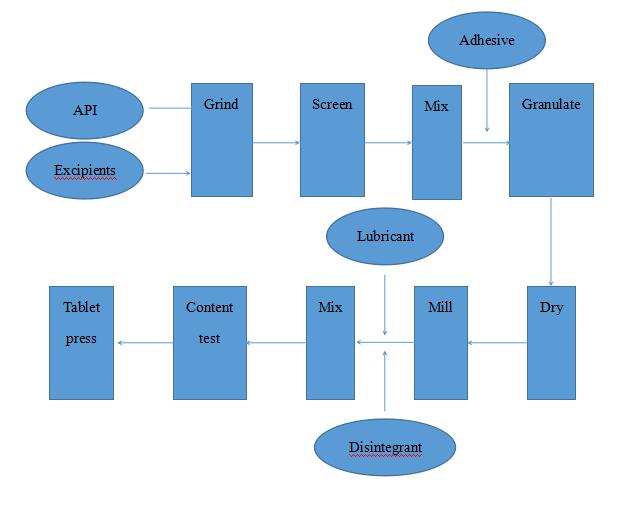
5) Technical flow chart
6) Wet granulation method
a. Squeezing granulation
b. Rotary granulation
c. High speed mixer granulation
d. Fluid bed granulation
e. Compound granulation
7) Squeezing granulation
a. Materials are mixed with adhesive and then the mixture is granulated after being squeezed through screen.
b. Key point
a) Mixtures should be agglomerated when gripped and dispersed when pressed.
b) Machines
i. Oscillating granulator
ii. Screw squeezing granulator
iii. Rotary squeezing granulator
c) Mixing is the key, during which adhesive should be of proper concentration and dosage.
d) Granularity is determined by screen hole size. Granules are cylindrical and their size is uniformly distributed.
e) Loose granules are produced under small squeezing force, which are suitable for tablet press.
f) This method is of multiple processes, poor reproducibility and requires high labor intensity. Therefore, it is not suit for mass production.
8) Rotary granulation
a. Mixed materials are put into containers and then adhesive is sprayed into the container or bottom plate which is rotating to form spherical granules.
b. Tilting rotary granulation pot, also known as round-plate granulator.
c. Centrifugal granulation machine
d. Master core forming
e. Master core growing
f. Pressing
9) High speed mixing
a. Materials are mixed uniformly with adhesive in a container and in high speed so that granules are produced.
b. Principle: The stirring paddle disperses adhesive and mixes it with materials. Then materials and adhesive are thrown to the device wall and moves upwards due to the centrifugal force generated by rotation. Large granules are made. Afterwards, the cutter grinds and cuts those large granules. Through the coordination between paddle and cutter, dense and uniform granules are produced by powerful extruding and rolling.
c. Features
a) Mixing, agglomeration and granulation process in a container.
b) Simplified process, low labor intensity, easy and quick operation.
c) It can produce not only dense and intense granules which can be used for capsule, but also loose granules which are ready for tablet press.
d) Wide application.
10) Fluid bed granulation
a. In the container, air flows upwards to keep powdery materials fluidized and suspending in the container, while liquid adhesive is being sprayed into to granulate powders.
b. Mixing, granulation and drying are finished in an equipment, so it is also known as one-step granulation.
c. Simplified process, time saving and low labor intensity.
d. Porous and soft granules of uniform size distribution, good fluidity and compressibility.
11) Drying
a. Wet granules are dried to remove moisture, avoid agglomeration or out-of-shape.
b. Drying temperature: generally 40-60°C, and 70-80°C for thermally stable drug substances.
c. Drying degree: Moisture content of dry granules is normally 3%.
d. Drying equipment
a) Box dryer
i. Simple equipment for drying in small batch;
ii. High labor intensity and energy consumption;
iii. Fierce migration of soluble ingredients.
b) Fluid bed dryer
i. High drying speed;
ii. Suitable for materials sensitive to temperature;
iii. Weak migration of soluble ingredients.
12) Milling and mixing
a. Milling
a) Separating agglomerated or bound granules.
b) Milling through screen: hole diameter ≤ hole diameter of granulation screen
b. Granule testing
a) API content
b) Water content
c. Mixing
a) General mixing: lubricant and disintegrant are added;
b) For volatile ingredients: fine powder adsorption and mixing then;
c) For API of small dosage or API sensitive to humidity and temperature: dissolving them in ethanol, spraying the solution on blank dry granules, pressing granules after several-hour sealing and storing. This method is known as blank granule method.
13) Tablet press - tablet weight calculation
a. According to API content
Tablet weight=API content/API proportion in granules
b. According to total weight of dry granules
Tablet weight=(dry granule weight + excipient weight)/tablet quantity
14) Tablet machine
a. According to structure: single punch tablet press vs. rotary tablet press
b. According to tablet shape: round tablet press vs. irregular tablet press
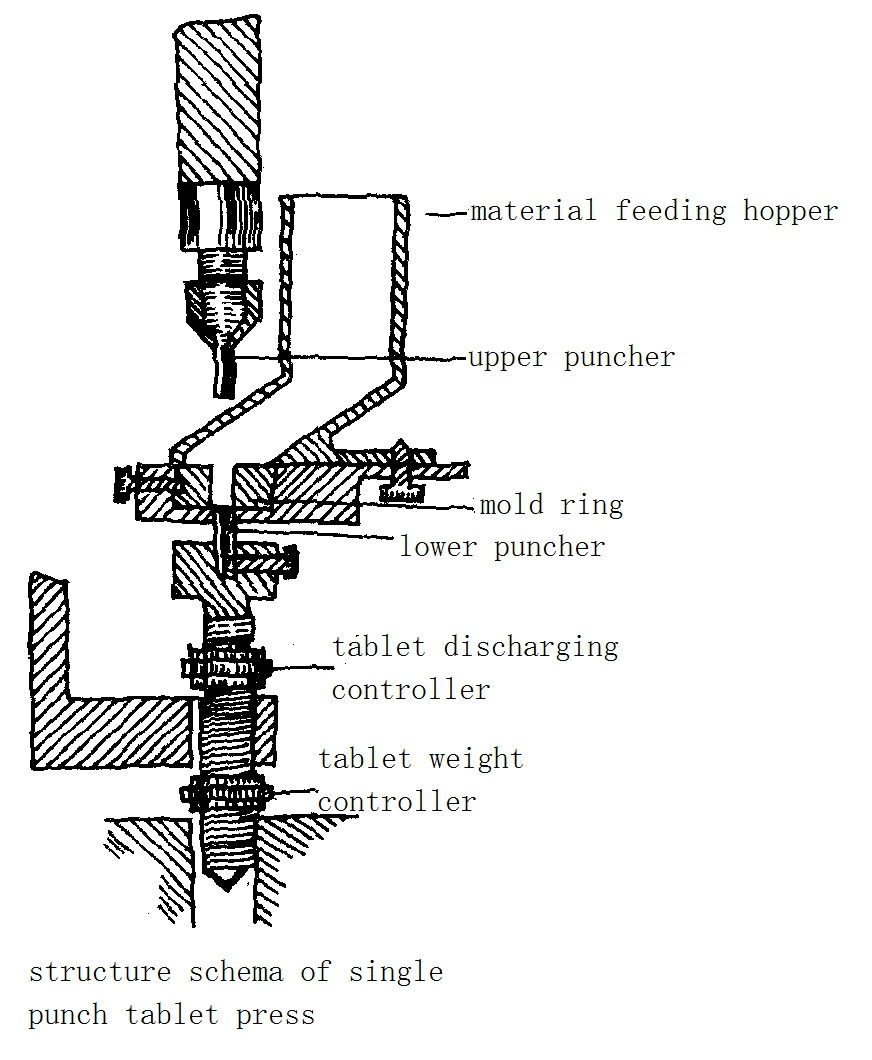
15) Single punch tablet press
16) Rotary tablet press
a. Tablet press process: filling - tablet pressing - tablet discharging
b. Advantages
a) High production efficiency: A machine might have 16, 19, 27, 33, 55 or even 75 punches. The machine of 55 punches can product 550,000 pcs tablets per hour.
b) The upper and lower punchers are pressed at the same time to distribute pressure uniformly and reduce tablet breaking possibility.
c) The material feeding hopper is fixed for material feeding time saving, uniformly mold hole filling and narrow weight distribution.
d) Pressure increases slowly to avoid tablet breaking.