Powder Mixing Technologies and Machines
Writer: admin Time:2020-07-13 14:24 Browse:℃
Powder mixing machines are always used to mix two or more kinds of powder in pharmaceutical industry, especially in tablet or capsule production. Since pharmaceutical industry is pretty special, some principle or requirements should be followed for powder mixing machine selection. Otherwise, the machine cannot play its role perfectly. To find out a suitable mixing machine, it’s necessary to have some basic knowledge about it.
1. What is powder mixing?
Mixing is a process to uniform ingredients as much as possible. And powder mixing refers to the process during which two or more than two kinds of powder are mixed for uniform proportion. Besides, little amount of liquid can also be added into powder mixing.
1) Mixing principle
Classified by status and operations during mixing, there can be three types of material movements:
a. Convection: particles move vertically and horizontally relatively;
b. Expansion: particles moves onto the surface of newly emerging powder;
c. Shearing: powder forms slip plane.
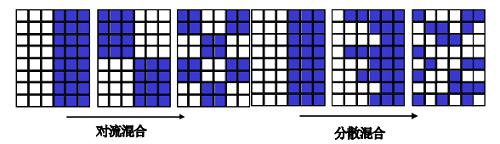
Convection mixing/expansion mixing
During powder mixing, convection, shearing and expansion will not appear individually, but function together (as shown in the following figure) in different area and based on one type. For powder mixing machine in pharmaceutical industry, powder is mainly mixed by convection, during which particles move up and down, left and right.
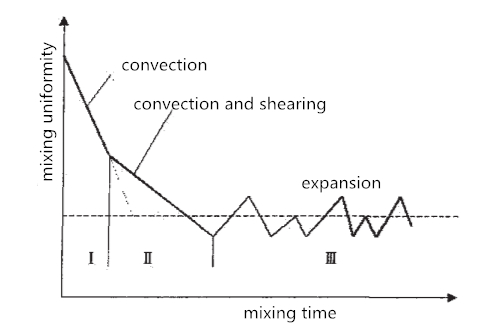
2. Influence of mixing uniformity on medical powder
Solid preparations are usually produced from multiple ingredients, including API and some other excipients. To ensure their uniformity, these ingredients should be ground, screened and then mixed. And mixing uniformity will directly affect distribution of API and further influence medicine efficacy.
1) Factors influencing mixing uniformity:
a. Particle size
Coarse particles are of good compressibility but poor formability and fine powdery particles are exactly the opposite. Proper proportion of coarse and fine particles can better powder filling, improve its comprssibility and agglomeration. However, different size of these particles challenge mixing because fine powder will attach to each other, hinder relative movement of particles and decrease uniformity.
b. Bulk density
The larger bulk density is, the more difficult mixing will be. Powder of low bulk density will float throughout mixing so that it is difficult for it to be mixed with powder of high bulk density.
c. Fluidity
Particles of poor fluidity will attach to each other easily, which has effect on powder convection and uniform mixing.
d. Particle shape
Particles of irregular shape or coarse surface are difficult to be mixed uniformly. But if they can be mixed uniformly, their state will be kept easily. Compared with them, smooth particles will separate out easily due to their strong fluidity.
e. Static electricity and surface energy
If air is pretty dry (e.g., relative humidity < 40%), static electricity will be generated and gathers powder.
Except the above factors, mixing uniformity will also be influenced by moisture content, fragility, angle of repose, agglomeration and elasticity...
3. Powder mixing machine
There are many powder mixing machines and can be generally classified into three types: compound, rotary or multi-directional. Each has its own features and advantages.
1) Rolling mixer (single-directional mixer)
Rolling mixer is classified into compound mixing machine and consists of material barrel, driving system and machine seat...
Principle: driven by motor, the barrel rotates in uniform speed. Several special boards are welded on internal barrel wall. They can push material to rotate along barrel wall up and down, right and left. At the same time, certain angle of boards against central axis can make material move back and forth. As a result, material can be completely mixed.
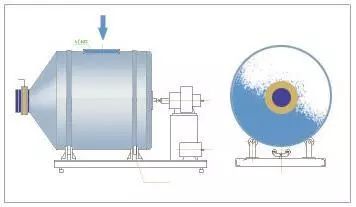
Rolling mixer
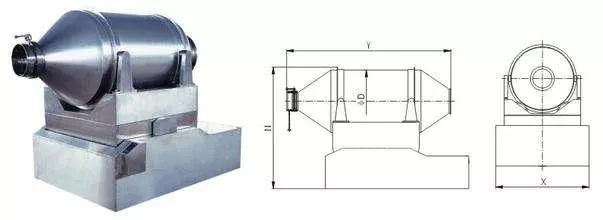
2) Rocking mixer (double-directional mixing machine)
Rocking mixer is also a compound mixer. It is composed of material barrel, two sets of barrel motion structure, upper and lower machine frame for the structure installation.
Principle: on the one hand, mixing barrel is driven by circular motion driving structure to move circularly along its symmetric axis. On the other hand, it is also driven by rocking driving structure to rotate and oscillate along the horizontal axis which is orthogonal against the symmetric axis. Meanwhile, the welded boards can throw material to increase its radial movement. At last, material can be mixed completely.
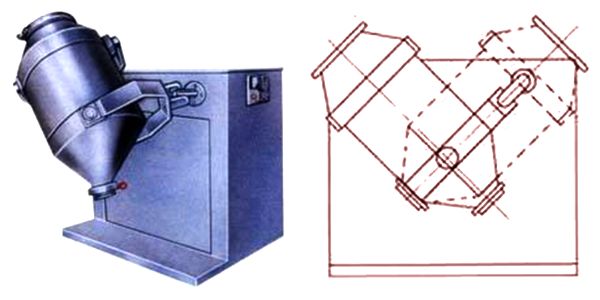
3) Three-dimensional mixer (universal mixing machine)
3D mixer is rotary. It is made up of machine seat, driving device, universal rocker structure, mixing barrel, electrical cabinet and so on. Besides, driving device consists of a driving shaft and a driven shaft, each with a Y-type universal joint. The mixing barrel is installed and connected with the two joints.
Principle: the mixing barrel can both rotate and revolve. This means that its motion is a compound of four types, namely: rotation along the central axis, up and down movement of two barrel ends, left and right movement of two barrel ends and translation movement of the barrel itself. Therefore, material in the barrel can rotate, roll, translate and fall down complexly. The process can generate alternating pulse and turbulence. The energy change during mixing pushes material to be in different motion and change their position frequently. At last, perfect mixing is achieved.
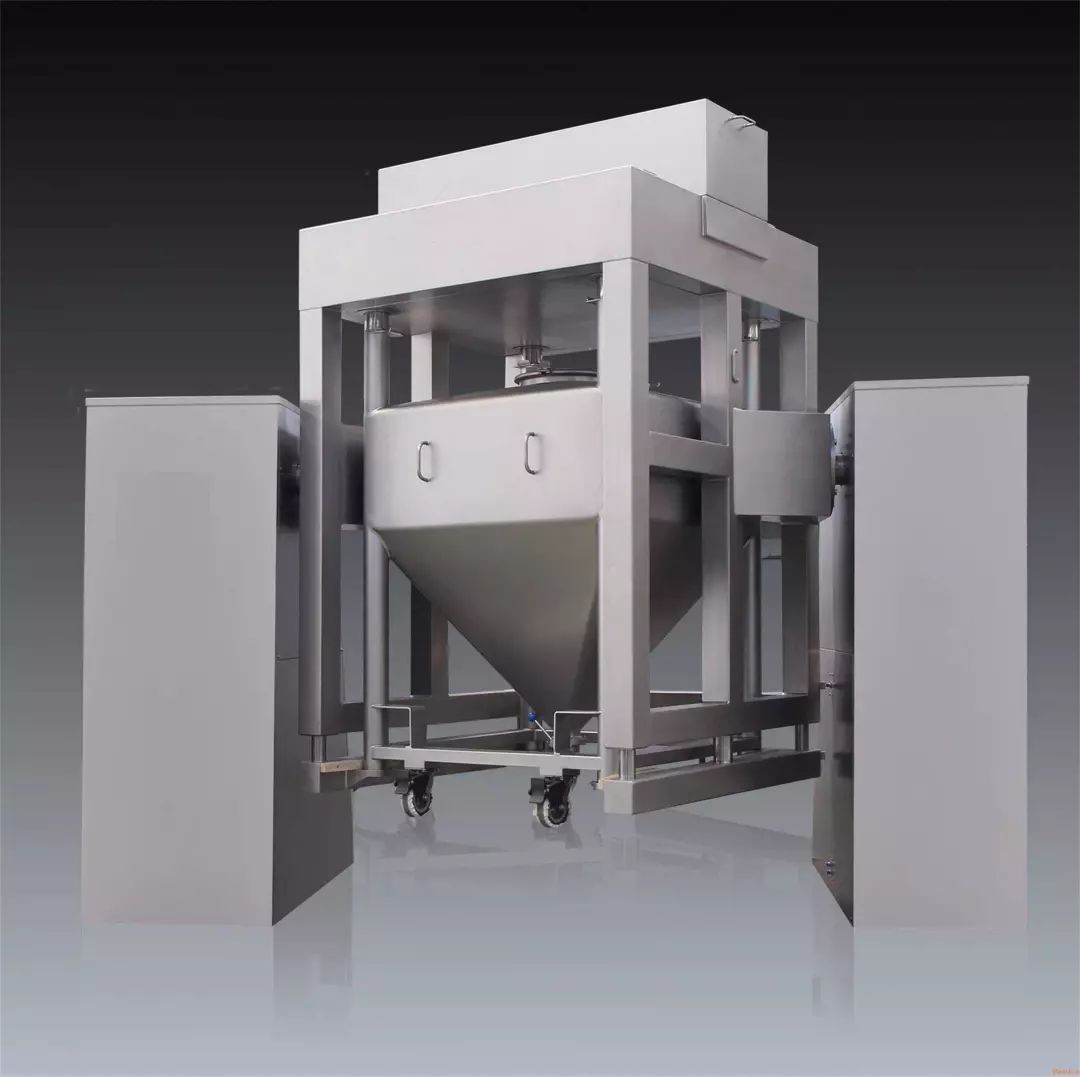
4) Bin blender
Bin (or square cone) blender is composed of machine frame, hopper, driving system, lifting system, braking system and control system. It is similar to multi-directional mixer.
Principle: this mixer makes use of the angle between overturning hopper and single holding shaft to rotate material. During the process, material overturns, changes size and mixes for uniform mixing. In addition, the hopper forms an angle against the rotation axis so that fierce overturning and tangential motion during the process can help achieve ideal mixing performance.

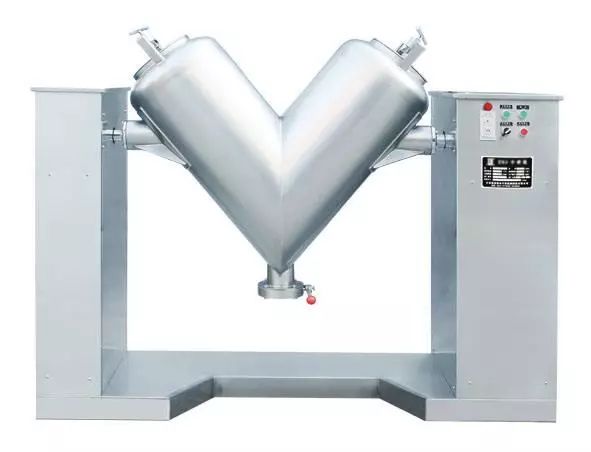
5) V-blender
V-blender separate and agglomerate material repeatedly. There are two types of V-blender:
a. Symmetric V-blender
Its shortages are high rotation height, dead corners and crossing contamination existing on the welding of two barrels, incomplete cleaning, horizontal and vertical motion only and long mixing time.
b. Asymmetric V-blender
The vessel is asymmetric. Its advantage is that material can be mixed repeatedly for high mixing efficiency. However, it has some shortages, including large size, large rotation space, dead corners and crossing contamination due to incomplete polishing of inner wall. Regardless of these shortages, this asymmetric V-blender is still adopted by some pharmaceutical enterprises.

6) Biconical mixer
This machine can only move to a single direction. Material cannot be mixed completely. For this reason, this machine is not popular among nowadays’ pharmaceutical factories.
7) Planetary conical mixer
Planetary conical mixer can be single- or double-spiral. It consists of cone, spiral rod and driving system. While mixing, the spiral rod can rotate and revolve at the same time.
Principle: rotation of spiral rod lift material and form material into a flow. Simultaneously, spiral rod revolves so that material outside can be a part of the flow. Material inside the cone can be mixed continuously and falls down at the center of the cone. As a result, it costs shorter time to mix material.



